-
Nieuws Feed
- EXPLORE
-
Pagina
-
Blogs
-
Forums
Confirmed! Comet 3I/ATLAS Is Indeed An Interstellar Visitor, Quite Different From Its Predecessors
Confirmed! Comet 3I/ATLAS Is Indeed An Interstellar Visitor, Quite Different From Its Predecessors
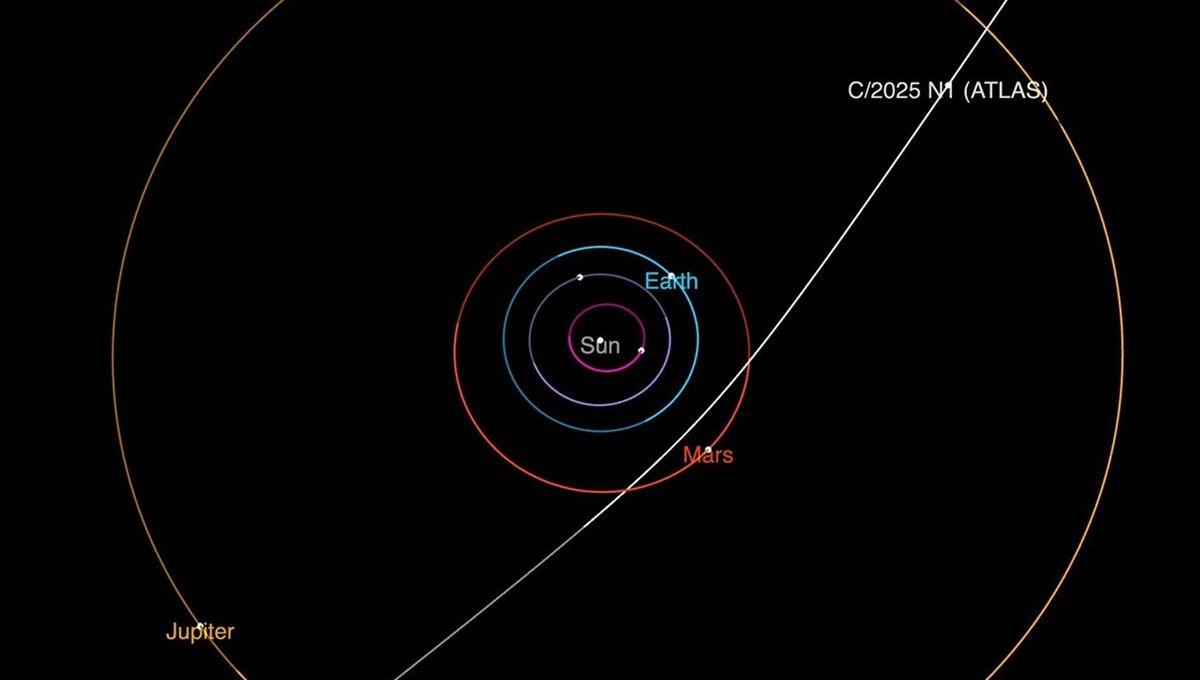
On July 1, the ATLAS (Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System) survey telescope reported the discovery of A11pl3Z, an object whose orbit looked like it came from another star. Now we know that this is indeed the case. The interstellar object has been given the name 3I/ATLAS, and we now know it's a comet.
The object, which is also known as C/2025 N1 (ATLAS), is moving almost twice as fast as the previous two interstellar objects that were caught visiting the Solar System. ’Oumuamua, discovered in 2017, moved at about 26.33 kilometers (16.36 miles) per second, while Comet 2I/Borisov, discovered in 2021, was moving a tad faster at 32.2 kilometers ( 20 miles) per second. 3I/ATLAS appears to be moving at around 58 kilometers (36 miles) per second. The first observations also suggest a much larger interstellar object compared to the first two. The cigar-shaped ‘Oumuamua was between 100 and 1,000 meters (328 and 3,280 feet) on its longest axis, and Comet Borisov had a nucleus of less than half a kilometer, despite producing a tail 14 times larger than Earth. Initial observations put 3I/ATLAS at 20 kilometers based on its brightness, but since it is a comet, this might not end up being correct, so more observations are needed. “The interstellar comet’s size and physical properties are being investigated by astronomers around the world. 3I/ATLAS should remain visible to ground-based telescopes through September, after which it will pass too close to the Sun to observe. It is expected to reappear on the other side of the Sun by early December, allowing for renewed observations,” NASA said in a statement. The initial discovery was met with a flurry of excitement, and observations have already been taken from across the world to better understand this object. It has also been found in archival observations, which have helped refine some of its properties. Image Credit: Gianluca Masi “Since that first report, observations from before the discovery have been gathered from the archives of three different ATLAS telescopes around the world and the Zwicky Transient Facility at the Palomar Observatory in San Diego County, California. These 'pre-discovery' observations extend back to June 14. Numerous telescopes have reported additional observations since the object was first reported,” NASA said. Comet 3I/ATLAS will get as close as 210 million kilometers (130 million miles) from the Sun, far beyond the orbit of Earth, on October 30, 2025. The interstellar interloper will be visible from Earth until September, then it will be behind the Sun from our point of view. It should then be back being visible in December. Previous estimates place about 10,000 interstellar objects within the orbit of Neptune on any given day. Most of these are too dark to be spotted by our telescopes, but they are likely there. Observatories, like the new Vera C. Rubin, which has recently demonstrated that it can discover over 2,000 new asteroids in a matter of hours, will likely help find a lot more objects.


