-
Feed de notícias
- EXPLORAR
-
Páginas
-
Blogs
-
Fóruns
As Solar Storm Hits Earth NASA Finds "The Sun Is Slowly Waking Up"
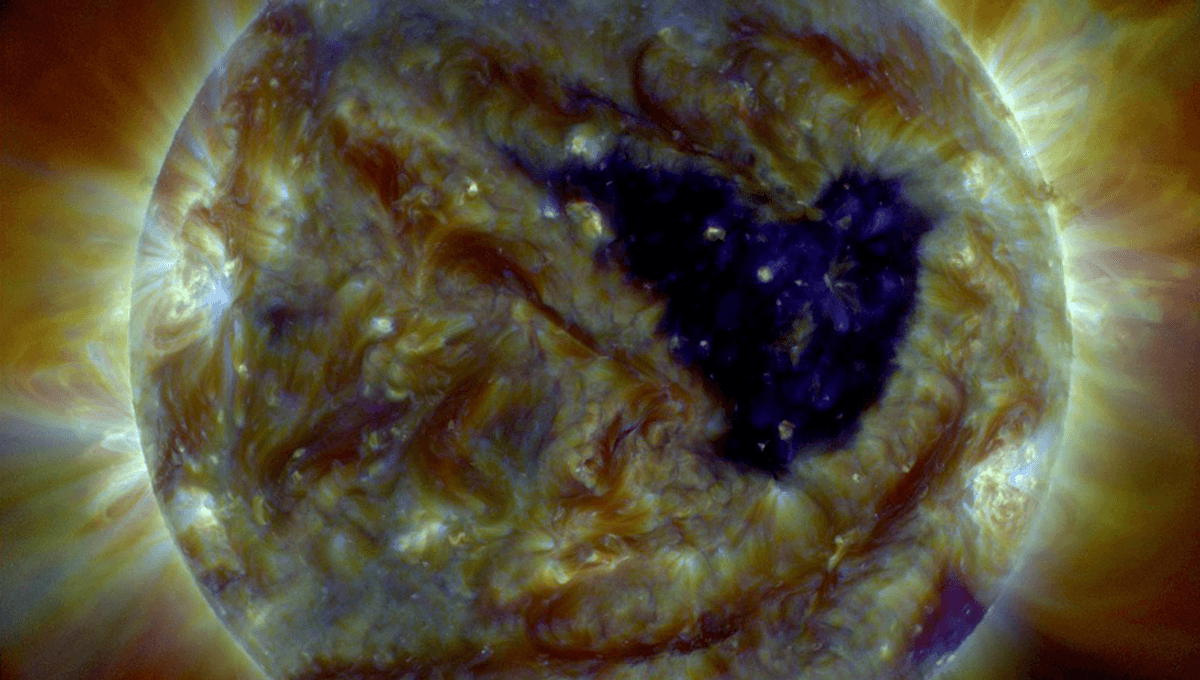
As Solar Storm Hits Earth NASA Finds "The Sun Is Slowly Waking Up"
A new NASA study has found that the Sun's activity is ramping up, reversing the trend and surprising astronomers.
The rest of this article is behind a paywall. Please sign in or subscribe to access the full content. Humans have known about sunspots since around 800 BCE, when ancient Chinese astronomers recorded observations of them in I Ching, the Book of Changes. "Sunspots are areas where the magnetic field is about 2,500 times stronger than Earth's, much higher than anywhere else on the Sun," the National Weather Service explains. "Because of the strong magnetic field, the magnetic pressure increases while the surrounding atmospheric pressure decreases. This in turn lowers the temperature relative to its surroundings because the concentrated magnetic field inhibits the flow of hot, new gas from the Sun's interior to the surface. " Following the invention of the telescope in 1608, astronomers have kept much better track of these sunspots, and noticed that they didn't appear at random, but increased and decreased in number over the years. Solar activity was found to increase and decrease over the roughly 11-year solar cycle – also known as the Schwabe cycle, named after the astronomer who first noticed it. From 1826 to 1843, German amateur astronomer Heinrich Schwabe observed the Sun, discovering that it rotates on its axis once every 27 days. He realized that over the course of 11 years, the Sun goes from quiet periods, where no sunspots can be seen, to the maximum phase, where 20 or more groups of sunspots can be seen. Despite a lot of study, there are still plenty of mysteries to solve about the solar cycle, driven by the Sun's magnetic field. For a start, the solar cycles are not uniform in length, and some appear much stronger or weaker than others. As well as this, there have been periods – for instance from 1645 to 1715, and from 1790 to 1830 – when the Sun was unusually quiet, and other longer-term trends. “We don’t really know why the Sun went through a 40-year minimum starting in 1790,” Jamie Jasinski of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, and lead author of the new study, explained in a statement. “The longer-term trends are a lot less predictable and are something we don’t completely understand yet.” That team has given us a new puzzle. Since the 1980s and up until 2008, solar activity had been steadily decreasing, before solar activity became the weakest on record. Astronomers believed that this was the Sun entering a period of very low activity dubbed the "deep solar minimum". But the new study has found that this is not the case. “All signs were pointing to the Sun going into a prolonged phase of low activity,” Jasinski added. “So it was a surprise to see that trend reversed. The Sun is slowly waking up.” "The trend of declining solar wind ended, and since then plasma and magnetic field parameters have steadily been increasing." While it's good to know a little more about the Sun's activity, and everybody loves seeing the aurora, an increase in activity isn't necessarily the best news for the Earth. Solar storms can cause radio blackouts, power grid failures, and even cause satellites to rain down on the planet. According to the team's findings, we could be in for more solar activity than we were expecting in the near future. "Comparison of values from a fitted trend to data between 2008 and 2025 show the following increases in solar wind proton parameters: speed (~6%), density (~26%), temperature (~29%), thermal pressure (~45%), mass flux (~27%), momentum flux or dynamic pressure (~34%), energy flux (~40%), interplanetary magnetic field magnitude (~31%), and the radial component of the magnetic field (~33%)," the team explains in their paper. "This has important implications on long-term solar trends, implying that the exceptional weakness of solar cycle 24 was most likely a recent outlier and that the Sun is not entering a modern era Maunder/Dalton-like minimum phase in its solar variation, but is instead recovering from a ~20 yr decline." The study is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.


