Meet The Dragon Prince, A New Dinosaur That’s Rewriting What We Know About Tyrannosaur Evolution
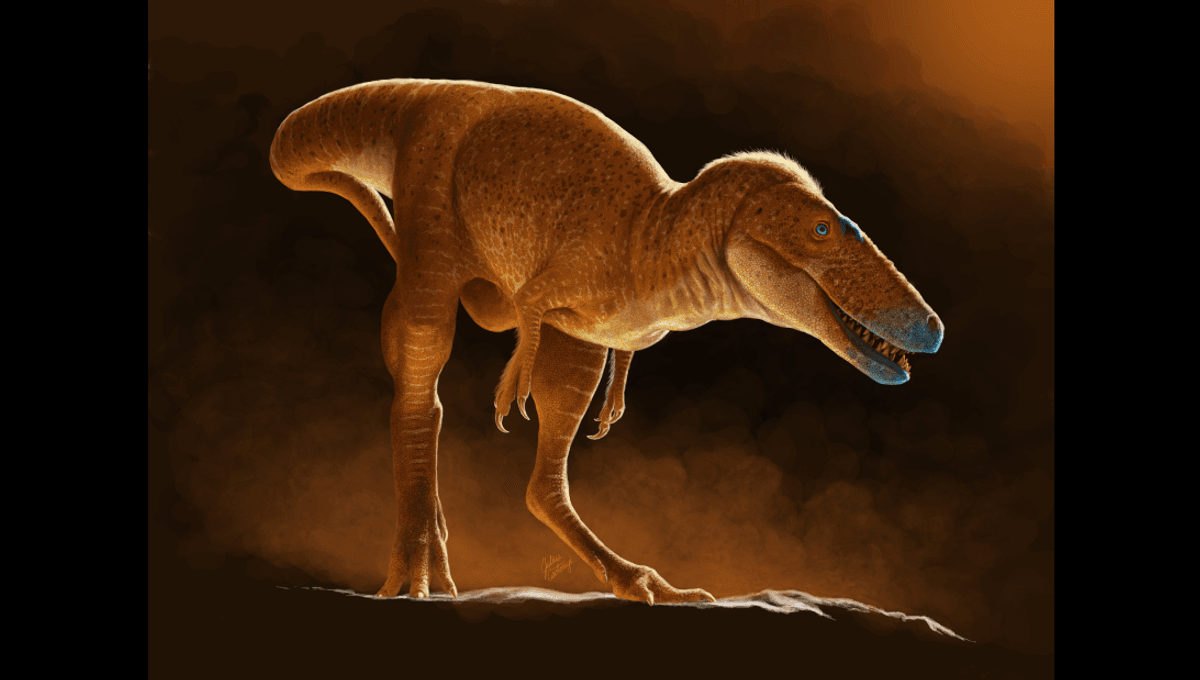
“What Started As The Discovery Of A New Species Ended Up With Us Re-Writing The Family History Of Tyrannosaurs”
A new species of dinosaur has been discovered in Mongolia, and it’s palaeontological royalty. Named Khankhuuluu (pronounced khan-KOO-loo) after the Mongolian for “dragon prince”, it represents the closest known ancestor to tyrannosaurs and has inspired a team of scientists to rewrite the evolutionary history of this iconic group of dinosaurs.
The dragon prince, or Khankhuuluu mongoliensis to you, was a relatively small species (compared to the monsters that came next) that weighed around 750 kilograms (118 stone). It was about 4 meters (13 feet) long and 2 meters (6.6 feet) at the hips, as informed by fossils recovered in the Upper Cretaceous deposits of Mongolia. The species represents the closest known ancestor to tyrannosaurs, marking the shift that saw smaller tyrannosauroid species in Asia migrate to North America and give rise to larger tyrannosaurs around 85 million years ago. Khankhuuluu is a missing link. Dr Darla Zelentisky When we think of tyrannosaurs, we tend to think of the absolute beasts like Tyrannosaurus rex, but there are some miniature models that exist in the fossil record. Adorably known as “Pinocchio” rexes (because they have long, slender snoots), these comparatively miniature tyrannosaurs were one of two closely related subgroups that emerged after a tyrannosaur lineage travelled from North America to Asia around 78 million years ago. Must've been like going back to its roots. The second group that emerged after that trip looked very different indeed, being the weighty giants like Tarbosaurus. It wasn’t until right at the very end of the tyrannosaur story, around 68 million years ago, that one of these giants stomped back to North America (make up your minds, guys), giving rise to T. rex. It took multiple migrations between Asia and North America to get there, but it all began with Khankhuuluu. The skeleton of Khankhuuluu mongoliensis. Image credit: Jared Voris For a long time, it was thought that Pinocchio rexes (scientifically known as alioramins) were examples of primitive tyrannosaurs, but this new-to-science species reveals that they were actually a unique and highly evolved tyrannosaur group that miniaturized despite being so closely related to giants. Therefore, the discovery of Khankhuuluu doesn’t just mark a new species, but a whole new perspective for understanding the tyrannosaur family tree. 'Pinocchio' rexes turned out to be highly evolved and their closest kin were actually the giant tyrannosaurs like T. rex and Tarbosaurus. Dr Darla Zelenitsky “Khankhuuluu is a missing link between small species that were around 200 kilograms (31.5 stone) and the tyrannosaurs that weighed way over 1,000 kilograms (157.4 stone),” study co-author Dr Darla Zelenitsky, Associate Professor at the University of Calgary, told IFLScience. “This discovery forced us to look at the tyrannosaur family tree in a very different light. Before this, there was a lot of confusion about who was related to who when it came to the many tyrannosaur species.” “Smaller species were mostly thought to be primitive/ancestral and larger species more evolved. We figured out it wasn’t quite that way. Small species of tyrannosaurs called alioramins (popularly called Pinocchio rexes) turned out to be highly evolved and their closest kin were actually the giant tyrannosaurs like T. rex and Tarbosaurus.” “This scenario is kind of like the little pygmy hippos today, where their closest kin are the massive river hippos. We had an astonishing result, but it made sense and has cleaned up some of the messiness of the tyrannosaur family tree. With what started as the discovery of a new species ended up with us re-writing the family history of tyrannosaurs.” The study is published in the journal Nature.


